The Role of CT Scans in Neuro-Oncology
Computed Tomography (CT) scans play an important role in the diagnosis and management of neurological conditions, including brain and spinal disorders. While advanced imaging techniques such as MRI and PET-CT are often used in neuro-oncology, CT remains a valuable and sometimes preferred diagnostic tool in specific clinical situations.
What Is a CT Scan and How Is It Different from MRI?
A CT scan uses X-rays and computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. It is fast, widely available, and particularly effective at detecting bone abnormalities, acute bleeding, calcifications, and skull fractures.
In contrast, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves rather than radiation. MRI provides superior soft tissue detail and is often preferred for evaluating brain tumors, spinal cord lesions, and subtle changes in brain structure. However, MRI exams typically take longer and may not be suitable for all patients, such as those with certain implanted medical devices or severe claustrophobia.
When CT Is the Method of Choice
CT is often the first-line imaging method in urgent or emergency settings. It is commonly used to:
-
Rapidly assess patients with acute neurological symptoms, such as sudden headache, confusion, or loss of consciousness
-
Detect intracranial hemorrhage, brain swelling, or hydrocephalus
-
Identify calcified tumors, bone involvement, or skull base abnormalities
-
Evaluate patients who cannot undergo MRI
In these situations, CT provides fast, reliable information that can guide immediate clinical decisions.
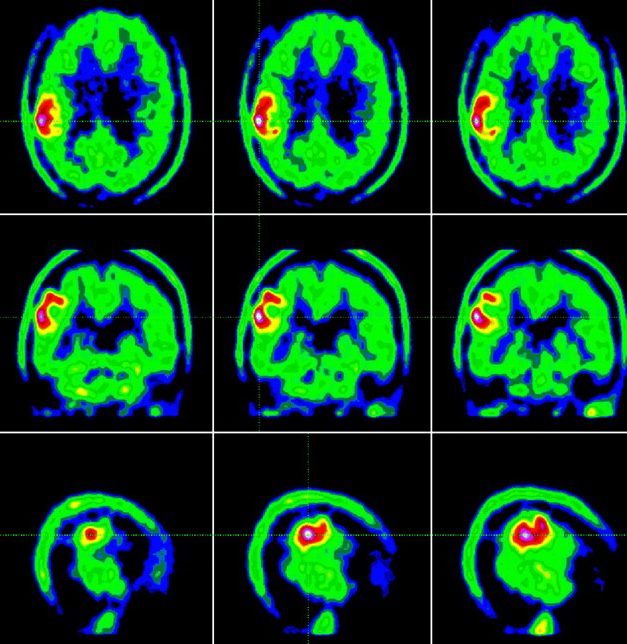
CT Compared with PET-CT
PET-CT combines metabolic imaging with anatomical detail, allowing clinicians to evaluate tumor activity, recurrence, or treatment response. While PET-CT is valuable in selected neuro-oncology cases, it is not typically used as an initial diagnostic tool.
Compared to PET-CT:
-
CT alone is faster, more accessible, and less expensive
-
CT excels at detecting structural changes, bleeding, and bone involvement
-
PET-CT provides functional and metabolic information but is usually reserved for complex cases, treatment planning, or suspected tumor recurrence
Each modality serves a specific purpose, and they are often complementary rather than competing tools.
The Importance of Expert Interpretation
Accurate diagnosis depends not only on imaging quality but also on expert interpretation. An experienced neuroradiologist can recognize subtle imaging features that distinguish tumors from other conditions, assess tumor aggressiveness, and identify treatment-related changes.
Equally important is close collaboration between radiologists and clinical specialists, including neurologists, neurosurgeons, and neuro-oncologists. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that imaging findings are interpreted in the context of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and treatment plan—leading to more accurate diagnoses and better clinical decisions.
Conclusion
CT scans remain a critical component of neuro-oncological imaging. Their speed, availability, and diagnostic reliability make them indispensable in emergency and selected clinical settings. When combined with expert radiological interpretation and multidisciplinary clinical evaluation, CT imaging supports timely diagnosis, safe treatment planning, and improved patient outcomes.
The article was medically reviewed by the Neuro-Oncology Team
Last update: December 14, 2025
Neuro-oncology Institute, Barcelona.